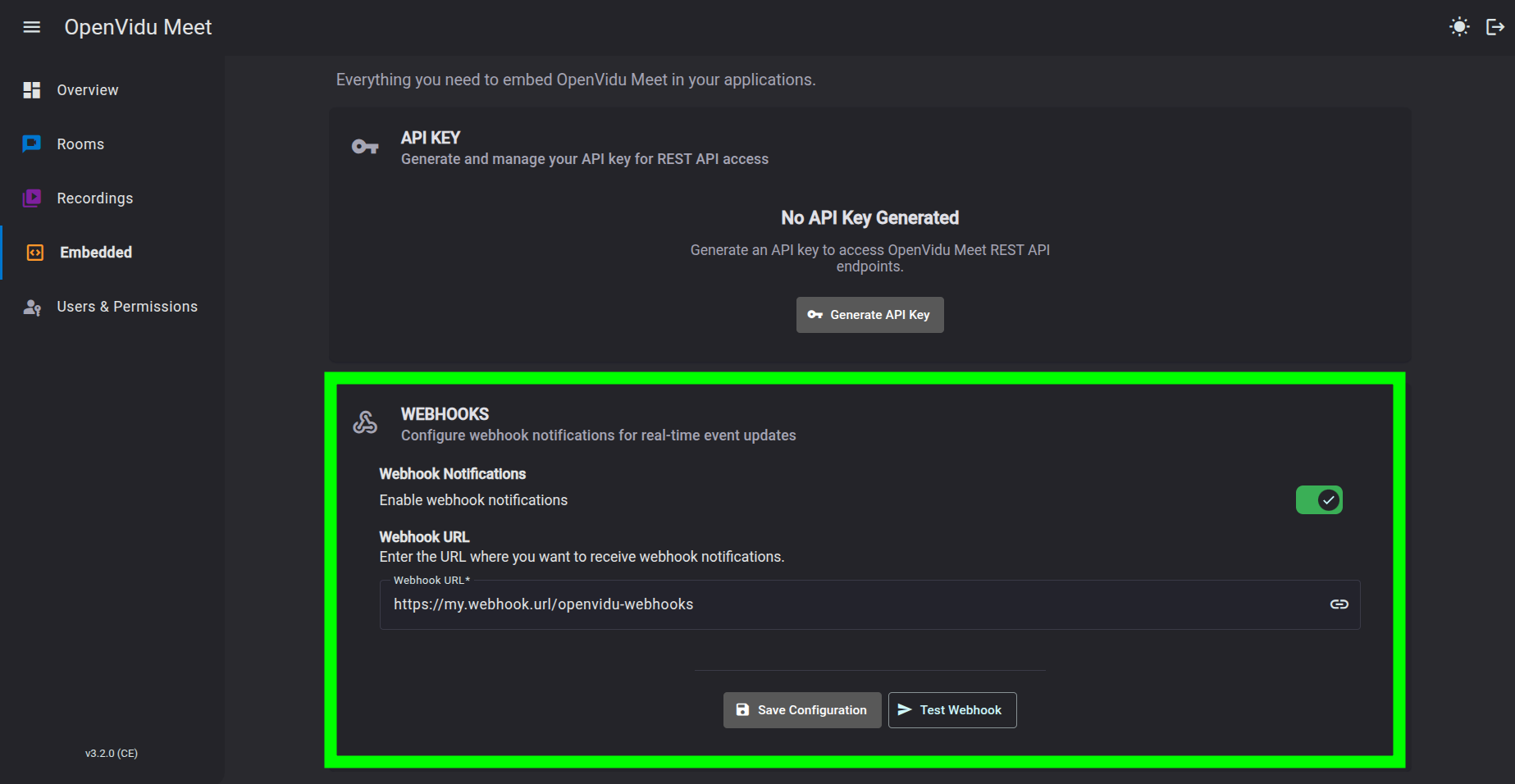
Webhooks#
OpenVidu Meet sends webhooks to inform about important events happening in a room. You can receive them in your application's backend and react accordingly with your own business logic.
Reference#
Visit OpenVidu Meet Webhooks reference documentation for a complete list of all available webhook events. They include:
Configuration#
You can configure webhooks in OpenVidu Meet in the "Embedded" page. There you can:
- Enable/Disable sending webhooks
- Set up your webhook endpoint URL
- Test the current webhook configuration with a fake event
Validate events#
OpenVidu Meet signs all webhook events with your API key, so you can verify their authenticity. This way you can ensure that the events received by your application's backend are coming from your actual OpenVidu Meet deployment and have not been tampered with.
Each webhook event includes two headers that you should use to validate the request:
x-signature: HMAC SHA256 signature of the request body, created by OpenVidu Meet using your API key.x-timestamp: Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) when the webhook was sent.
The steps to validate a webhook event in your backend are the following, given that you have access to the HTTP request body and headers:
- Get the
x-signatureandx-timestampheaders from the request. - Compare the
x-timestampheader value with the current Unix timestamp. If the difference is greater than a predefined threshold (e.g., 2 minutes), reject it to prevent replay attacks . - Concatenate in a single string the
x-timestampheader value + character.+ the JSON request body. - Create a HMAC SHA256 hash of the string of point 3) using your OpenVidu Meet API key as the key.
- Compare the computed hash of point 4) with the
x-signatureheader value. Do a time safe comparison to avoid timing attacks . If they match, the request is valid.
Below there are code snippets in different languages, showing the exact implementation of the above steps.
Checkout working example
import crypto from "crypto";
const OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY";
const MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE = 120 * 1000; // 2 minutes in milliseconds
function isWebhookEventValid(body, headers) {
const signature = headers["x-signature"]; // (1)!
const timestamp = parseInt(headers["x-timestamp"], 10);
if (!signature || !timestamp || isNaN(timestamp)) {
return false;
}
const current = Date.now();
const diffTime = current - timestamp;
if (diffTime >= MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE) { // (2)!
// Webhook event too old
return false;
}
const signedPayload = `${timestamp}.${JSON.stringify(body)}`; // (3)!
const expectedSignature = crypto // (4)!
.createHmac("sha256", OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY)
.update(signedPayload, "utf8")
.digest("hex");
return crypto.timingSafeEqual( // (5)!
Buffer.from(expectedSignature, "hex"),
Buffer.from(signature, "hex")
);
}
- 1) Get the
x-signatureandx-timestampheaders from the request. - 2) Compare the
x-timestampheader value with the current Unix timestamp. If the difference is greater than a predefined threshold (e.g., 2 minutes), reject it to prevent replay attacks . - 3) Concatenate in a single string the
x-timestampheader value + character.+ the JSON request body. - 4) Create a HMAC SHA256 hash of the string of point 3) using your OpenVidu Meet API key as the key.
- 5) Compare the computed hash of point 4) with the
x-signatureheader value. Do a time safe comparisson to avoid timing attacks . If they match, the request is valid.
Checkout working example
package com.example;
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.Map;
public class WebhookValidator {
private static final long MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE = 120 * 1000; // 2 minutes in milliseconds
private static final String OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY";
public static boolean isWebhookEventValid(Object body, Map<String, String> headers) {
String signature = headers.get("x-signature"); // (1)!
String ts = headers.get("x-timestamp");
if (signature == null || ts == null) return false;
long timestamp;
try {
timestamp = Long.parseLong(ts);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
return false;
}
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
long diffTime = current - timestamp;
if (diffTime >= MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE) { // (2)!
// Webhook event too old
return false;
}
String signedPayload = timestamp + "." + body.toString(); // (3)!
try {
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
mac.init(
new SecretKeySpec(
OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), // (4)!
"HmacSHA256"
)
);
byte[] expected = mac.doFinal(signedPayload.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
byte[] actual = hexToBytes(signature);
return timingSafeEqual(expected, actual); // (5)!
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
// Helper method to convert hex string to byte array
private static byte[] hexToBytes(String hex) {
int len = hex.length();
byte[] data = new byte[len / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 2) {
data[i / 2] = (byte) ((Character.digit(hex.charAt(i), 16) << 4)
+ Character.digit(hex.charAt(i + 1), 16));
}
return data;
}
// Time safe comparison to prevent timing attacks
private static boolean timingSafeEqual(byte[] a, byte[] b) {
if (a.length != b.length) return false;
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
result |= a[i] ^ b[i];
}
return result == 0;
}
}
- 1) Get the
x-signatureandx-timestampheaders from the request. - 2) Compare the
x-timestampheader value with the current Unix timestamp. If the difference is greater than a predefined threshold (e.g., 2 minutes), reject it to prevent replay attacks . - 3) Concatenate in a single string the
x-timestampheader value + character.+ the JSON request body. - 4) Create a HMAC SHA256 hash of the string of point 3) using your OpenVidu Meet API key as the key.
- 5) Compare the computed hash of point 4) with the
x-signatureheader value. Do a time safe comparisson to avoid timing attacks . If they match, the request is valid.
Checkout working example
package main
import (
"crypto/hmac"
"crypto/sha256"
"crypto/subtle"
"encoding/hex"
"encoding/json"
"net/http"
"strconv"
"time"
)
const (
maxWebhookAge = 120 * 1000 // 2 minutes in milliseconds
openviduMeetApiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY"
)
func isWebhookEventValid(bodyBytes []byte, headers http.Header) bool {
signature := headers.Get("x-signature") // (1)!
tsStr := headers.Get("x-timestamp")
if signature == "" || tsStr == "" {
return false
}
timestamp, err := strconv.ParseInt(tsStr, 10, 64)
if err != nil {
return false
}
current := time.Now().UnixMilli()
diffTime := current - timestamp
if diffTime >= maxWebhookAge { // (2)!
// Webhook event too old
return false
}
signedPayload := tsStr + "." + string(bodyBytes) // (3)!
mac := hmac.New(sha256.New, []byte(openviduMeetApiKey)) // (4)!
mac.Write([]byte(signedPayload))
expected := mac.Sum(nil)
actual, err := hex.DecodeString(signature)
if err != nil {
return false
}
return subtle.ConstantTimeCompare(expected, actual) == 1 // (5)!
}
- 1) Get the
x-signatureandx-timestampheaders from the request. - 2) Compare the
x-timestampheader value with the current Unix timestamp. If the difference is greater than a predefined threshold (e.g., 2 minutes), reject it to prevent replay attacks . - 3) Concatenate in a single string the
x-timestampheader value + character.+ the JSON request body. - 4) Create a HMAC SHA256 hash of the string of point 3) using your OpenVidu Meet API key as the key.
- 5) Compare the computed hash of point 4) with the
x-signatureheader value. Do a time safe comparisson to avoid timing attacks . If they match, the request is valid.
Checkout working example
import hmac
import hashlib
import json
import time
MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE = 120 * 1000 # 2 minutes in milliseconds
OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY"
def is_webhook_event_valid(body, headers):
signature = headers.get("x-signature") # (1)!
timestamp_str = headers.get("x-timestamp")
if not signature or not timestamp_str:
return False
try:
timestamp = int(timestamp_str)
except ValueError:
return False
current = int(time.time() * 1000)
diff_time = current - timestamp
if diff_time >= MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE: # (2)!
return False
json_body = json.dumps(body, separators=(",", ":"))
signed_payload = str(timestamp) + "." + json_body # (3)!
expected = hmac.new( # (4)!
OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY.encode('utf-8'),
signed_payload.encode('utf-8'),
hashlib.sha256
).hexdigest()
return hmac.compare_digest(expected, signature) # (5)!
- 1) Get the
x-signatureandx-timestampheaders from the request. - 2) Compare the
x-timestampheader value with the current Unix timestamp. If the difference is greater than a predefined threshold (e.g., 2 minutes), reject it to prevent replay attacks . - 3) Concatenate in a single string the
x-timestampheader value + character.+ the JSON request body. - 4) Create a HMAC SHA256 hash of the string of point 3) using your OpenVidu Meet API key as the key.
- 5) Compare the computed hash of point 4) with the
x-signatureheader value. Do a time safe comparisson to avoid timing attacks . If they match, the request is valid.
Checkout working example
<?php
const MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE = 120 * 1000; // 2 minutes in milliseconds
const OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY";
function isWebhookEventValid($body, $headers)
{
$signature = $headers['x-signature'] ?? null; // (1)!
$timestampStr = $headers['x-timestamp'] ?? null;
if (!$signature || !$timestampStr) {
return false;
}
$timestamp = filter_var($timestampStr, FILTER_VALIDATE_INT);
if ($timestamp === false) {
return false;
}
$current = intval(microtime(true) * 1000);
$diffTime = $current - $timestamp;
if ($diffTime >= MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE) { // (2)!
return false;
}
$signedPayload = $timestamp . '.' . json_encode($body, JSON_UNESCAPED_SLASHES); // (3)!
$expected = hash_hmac('sha256', $signedPayload, OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY); // (4)!
return hash_equals($expected, $signature); // (5)!
}
?>
- 1) Get the
x-signatureandx-timestampheaders from the request. - 2) Compare the
x-timestampheader value with the current Unix timestamp. If the difference is greater than a predefined threshold (e.g., 2 minutes), reject it to prevent replay attacks . - 3) Concatenate in a single string the
x-timestampheader value + character.+ the JSON request body. - 4) Create a HMAC SHA256 hash of the string of point 3) using your OpenVidu Meet API key as the key.
- 5) Compare the computed hash of point 4) with the
x-signatureheader value. Do a time safe comparisson to avoid timing attacks . If they match, the request is valid.
Checkout working example
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
using System.Text.Json;
public class WebhookValidator
{
private const long MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE = 120 * 1000; // 2 minutes in milliseconds
private const string OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY";
public static bool IsWebhookEventValid(string body, Dictionary<string, string> headers)
{
if (!headers.TryGetValue("x-signature", out var signature) || // (1)!
!headers.TryGetValue("x-timestamp", out var timestampStr))
{
return false;
}
if (!long.TryParse(timestampStr, out long timestamp))
{
return false;
}
long current = DateTimeOffset.UtcNow.ToUnixTimeMilliseconds();
long diffTime = current - timestamp;
if (diffTime >= MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE) // (2)!
{
return false;
}
string signedPayload = $"{timestamp}.{body}"; // (3)!
using (var hmac = new HMACSHA256(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY))) // (4)!
{
byte[] expected = hmac.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(signedPayload));
byte[] actual = Convert.FromHexString(signature);
return CryptographicOperations.FixedTimeEquals(expected, actual); // (5)!
}
}
}
- 1) Get the
x-signatureandx-timestampheaders from the request. - 2) Compare the
x-timestampheader value with the current Unix timestamp. If the difference is greater than a predefined threshold (e.g., 2 minutes), reject it to prevent replay attacks . - 3) Concatenate in a single string the
x-timestampheader value + character.+ the JSON request body. - 4) Create a HMAC SHA256 hash of the string of point 3) using your OpenVidu Meet API key as the key.
- 5) Compare the computed hash of point 4) with the
x-signatureheader value. Do a time safe comparisson to avoid timing attacks . If they match, the request is valid.
Checkout working example
require 'openssl'
require 'json'
MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE = 120 * 1000 # 2 minutes in milliseconds
OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY"
def webhook_event_valid?(body, headers)
signature = headers['x-signature'] # (1)!
timestamp_str = headers['x-timestamp']
return false if signature.nil? || timestamp_str.nil?
begin
timestamp = Integer(timestamp_str)
rescue ArgumentError
return false
end
current = (Time.now.to_f * 1000).to_i
diff_time = current - timestamp
return false if diff_time >= MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE # (2)!
signed_payload = "#{timestamp}.#{body.to_json}" # (3)!
expected = OpenSSL::HMAC.hexdigest('SHA256', OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY, signed_payload) # (4)!
OpenSSL.fixed_length_secure_compare(expected, signature) # (5)!
end
- 1) Get the
x-signatureandx-timestampheaders from the request. - 2) Compare the
x-timestampheader value with the current Unix timestamp. If the difference is greater than a predefined threshold (e.g., 2 minutes), reject it to prevent replay attacks . - 3) Concatenate in a single string the
x-timestampheader value + character.+ the JSON request body. - 4) Create a HMAC SHA256 hash of the string of point 3) using your OpenVidu Meet API key as the key.
- 5) Compare the computed hash of point 4) with the
x-signatureheader value. Do a time safe comparisson to avoid timing attacks . If they match, the request is valid.
Checkout working example
use chrono::Utc;
use hmac::{Hmac, Mac};
use sha2::Sha256;
use std::collections::HashMap;
type HmacSha256 = Hmac<Sha256>;
fn is_webhook_event_valid(body_str: &str, headers: &HashMap<String, String>) -> bool {
let signature = match headers.get("x-signature") { // (1)!
Some(sig) => sig,
None => return false,
};
let timestamp_str = match headers.get("x-timestamp") {
Some(ts) => ts,
None => return false,
};
let timestamp: i64 = match timestamp_str.parse() {
Ok(ts) => ts,
Err(_) => return false,
};
// Check timestamp age
let current = Utc::now().timestamp_millis();
let diff_time = current - timestamp;
if diff_time >= MAX_WEBHOOK_AGE { // (2)!
return false;
}
// Create signed payload using the raw body string
let signed_payload = format!("{}.{}", timestamp, body_str); // (3)!
// Calculate HMAC
let mut mac = match HmacSha256::new_from_slice(OPENVIDU_MEET_API_KEY.as_bytes()) { // (4)!
Ok(mac) => mac,
Err(_) => return false,
};
mac.update(signed_payload.as_bytes());
let expected = mac.finalize().into_bytes();
let expected_hex = hex::encode(expected);
// Timing-safe comparison
if signature.len() != expected_hex.len() {
return false;
}
let mut result = 0u8;
for (a, b) in signature.bytes().zip(expected_hex.bytes()) { // (5)!
result |= a ^ b;
}
result == 0
}
- 1) Get the
x-signatureandx-timestampheaders from the request. - 2) Compare the
x-timestampheader value with the current Unix timestamp. If the difference is greater than a predefined threshold (e.g., 2 minutes), reject it to prevent replay attacks . - 3) Concatenate in a single string the
x-timestampheader value + character.+ the JSON request body. - 4) Create a HMAC SHA256 hash of the string of point 3) using your OpenVidu Meet API key as the key.
- 5) Compare the computed hash of point 4) with the
x-signatureheader value. Do a time safe comparisson to avoid timing attacks . If they match, the request is valid.
Failures and retries#
OpenVidu Meet will automatically retry sending webhooks in case of failures. For example, if your server is down or returns an error response.
It will retry 5 times, with an exponential backoff (meaning it will wait longer between each retry).
Info
Your server must respond with a 2xx HTTP status code to acknowledge that you have received the webhook event. The timeout granted by OpenVidu Meet to do so is 5 seconds. If your server takes longer than that to respond, or if it sends any status code other than 2xx, OpenVidu Meet will consider it a failure and trigger a retry.