OpenVidu High Availability installation: Google Cloud Platform#
Google Cloud Platform
Info
OpenVidu High Availability is part of OpenVidu PRO. Before deploying, you need to create an OpenVidu account to get your license key. There's a 15-day free trial waiting for you!
This section describes how to deploy a production-ready OpenVidu High Availability setup on Google Cloud Platform. The deployed services are equivalent to those in the On Premises High Availability installation, but are provisioned as Google Cloud Platform resources and automated through the Google Cloud Console.
To deploy OpenVidu on Google Cloud Platform, log in to Infrastructure Manager in the GCP Console. Then follow the next steps and fill in your preferred parameters.
This is what the deployment architecture looks like:

- The Load Balancer distributes HTTPS traffic to the Master Nodes.
- If RTMP media is ingested, the Load Balancer also routes this traffic to the Master Nodes that they act as a bridge.
- WebRTC traffic (SRTP/SCTP/STUN/TURN) is routed directly to the Media Nodes.
- 4 fixed Virtual Machine Instances are created for the Master Nodes. It must always be 4 Master Nodes to ensure high availability.
- A Managed Instance Group of Media Nodes is created to scale the number of Media Nodes based on system load.
We use a custom scale-in strategy to allow the graceful shutdown of Media Nodes. In this way we ensure no disruption of active Rooms when the cluster tries to remove a Media Node.
- The Managed Instance Group (MIG) is set to Scale OUT only.
- We use a lambda function to check if the MIG current size is more than the recommended size that it targets.
- If the current size is more than the recommended size we calculate the number of instances that should scale in and we remove them from the MIG.
- The instances have a cron job that checks every minute if they are out of the MIG and runs the graceful shutdown script if they are out of the MIG.
Deployment details#
Info
We recommend to create a new project to deploy OpenVidu there, avoiding possible conflicts between resources. Enable Secrets Manager Api first in that project and then deploy the stack. You might need to deploy multiple times to let the APIs activate.
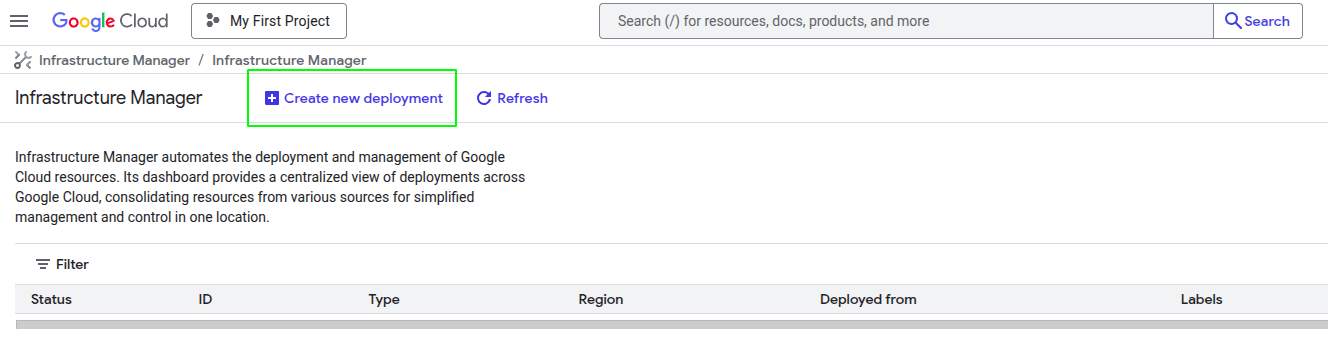
To deploy OpenVidu, first create a new deployment using the top-left button, as shown in the image.
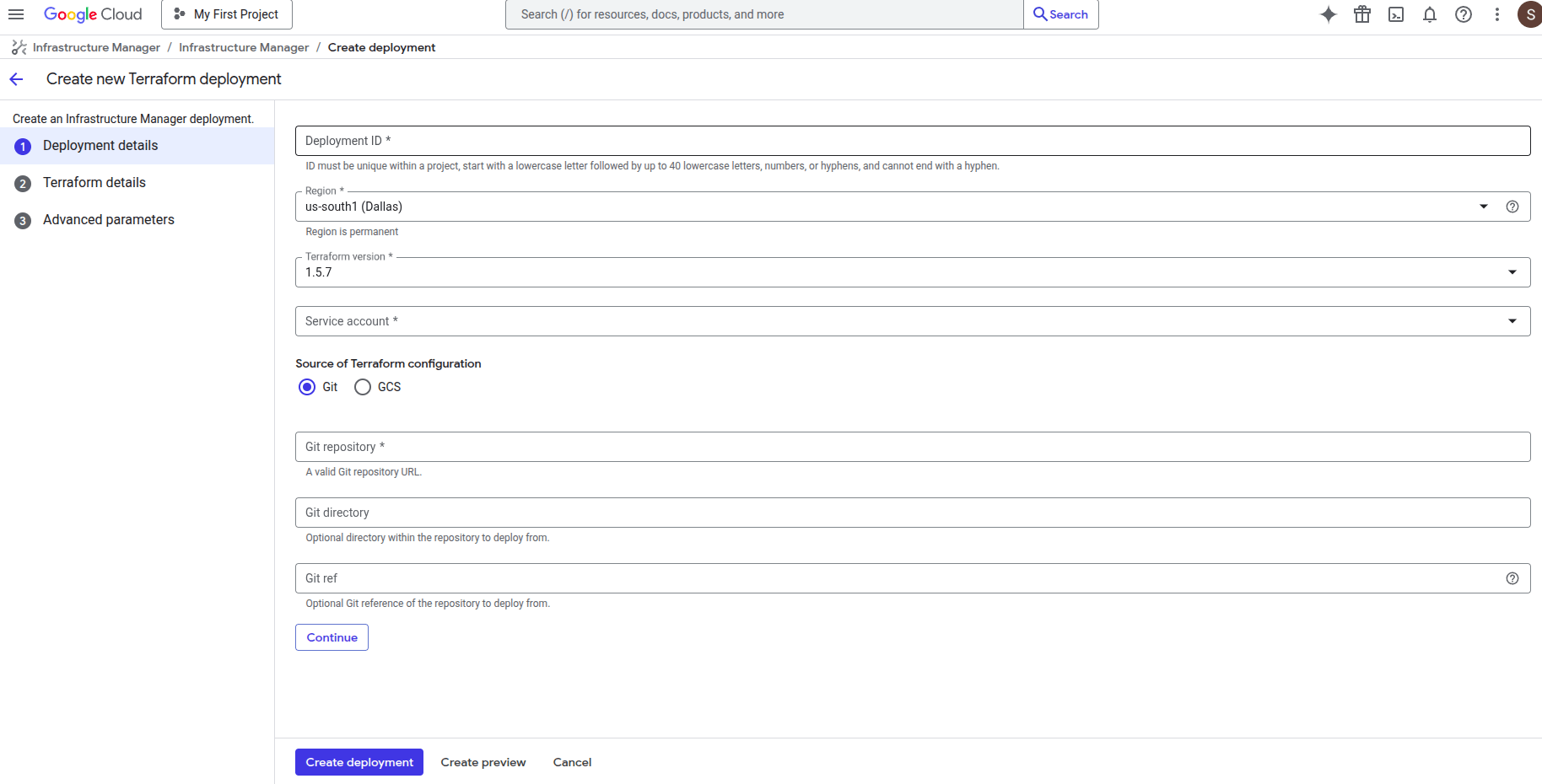
Once you click the button, you will see this window.
- Fill Deployment ID with any name you prefer (for example, openvidu-ha-deployment).
- Change the Region to the one you prefer.
Warning
If you change the region in the previous step, don't forget to update the region and zone in the Terraform values.
- Leave Terraform version as 1.5.7.
- For Service Account, you will need to create a new one with "Owner" permissions. To do this, click the "Service Account" label and then "New Service Account". Choose your service account name, click "Create and Continue", select the "Owner" role, click "Continue", and then "Done".
New Service Account Steps




- Fill Git repository with this link
https://github.com/OpenVidu/openvidu.git, which corresponds to our Git repository where the Terraform files to deploy OpenVidu are located. - Fill the Git directory with the following path
openvidu-deployment/pro/ha/gcp - For the Git ref, use
v3.6.0, corresponding to the version you want to deploy.
Finally, click Continue.
Input Values#
In Google Cloud Platform, there is no built-in template with parameters. You need to manually enter in the console the parameters declared in our Terraform files, so below is a detailed table of all optional and mandatory parameters.
Mandatory Parameters#
| Input Value | Description |
|---|---|
| projectId | GCP project id where the resources will be created. |
| stackName | Stack name for OpenVidu deployment. |
| openviduLicense | Your OpenVidu License. Get one here if you don't have one. |
Optional Parameters#
| Input Value | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| region | "europe-west2" | GCP region where resources will be created. |
| zone | "europe-west2-b" | GCP zone that some resources will use. |
| certificateType | "letsEncrypt" | Certificate type for OpenVidu deployment. Options:
Warning: sslip.io is currently experiencing Let's Encrypt rate limiting issues, which may prevent SSL certificates from being generated. It is recommended to use your own domain name. Check this community thread for troubleshooting and updates. |
| publicIpAddress | (none) | Previously created Public IP address for the OpenVidu Deployment. Blank will generate a public IP. |
| domainName | (none) | Domain name for the OpenVidu Deployment. |
| ownPublicCertificate | (none) | If certificate type is 'owncert', this parameter will be used to specify the public certificate in base64 format. |
| ownPrivateCertificate | (none) | If certificate type is 'owncert', this parameter will be used to specify the private certificate in base64 format. |
| initialMeetAdminPassword | (none) | Initial password for the 'admin' user in OpenVidu Meet. If not provided, a random password will be generated. |
| initialMeetApiKey | (none) | Initial API key for OpenVidu Meet. If not provided, no API key will be set and the user can set it later from Meet Console. |
| masterNodesInstanceType | "e2-standard-2" | Specifies the GCE machine type for your OpenVidu Master Node. |
| masterNodesDiskSize | 100 | Size of the disk in GB for master nodes |
| mediaNodeInstanceType | "e2-standard-2" | Specifies the GCE machine type for your OpenVidu Media Nodes. |
| initialNumberOfMediaNodes | 1 | Number of initial media nodes to deploy. |
| minNumberOfMediaNodes | 1 | Minimum number of media nodes to deploy. |
| maxNumberOfMediaNodes | 5 | Maximum number of media nodes to deploy. |
| scaleTargetCPU | 50 | Target CPU percentage to scale out or in. |
| GCSAppDataBucketName | (none) | Name of the GCS bucket to store application data and recordings. If empty, a bucket will be created |
| GCSClusterDataBucketName | (none) | Name of the GCS bucket to store cluster data. If empty, a bucket will be created |
| rtcEngine | "pion" | RTCEngine media engine to use. Allowed values are 'pion' and 'mediasoup'. |
| additionalInstallFlags | (none) | Additional optional flags to pass to the OpenVidu installer (comma-separated, e.g., '--flag1=value, --flag2'). |
For more details, you can check the variables.tf file to see additional information about the inputs.
Warning
It's important that you enter the input variables with the exact same names as they appear in the table, as shown in the next image.

Deploying the stack#
When you are satisfied with your input values, click "Continue" and then "Create deployment". The deployment will be validated and all resources will be created. Wait around 7 to 12 minutes for the nodes to install OpenVidu.
Warning
In case of failure, check the Cloud Build logs shown at the top of the screen and redeploy after applying the required changes. If the failure is related to an API, delete the deployment and create a new one. If it keeps failing, contact us.

When everything is ready, you can check the secrets on the Secret Manager or by connecting through SSH to the instances:
-
Go to the Secret Manager .
-
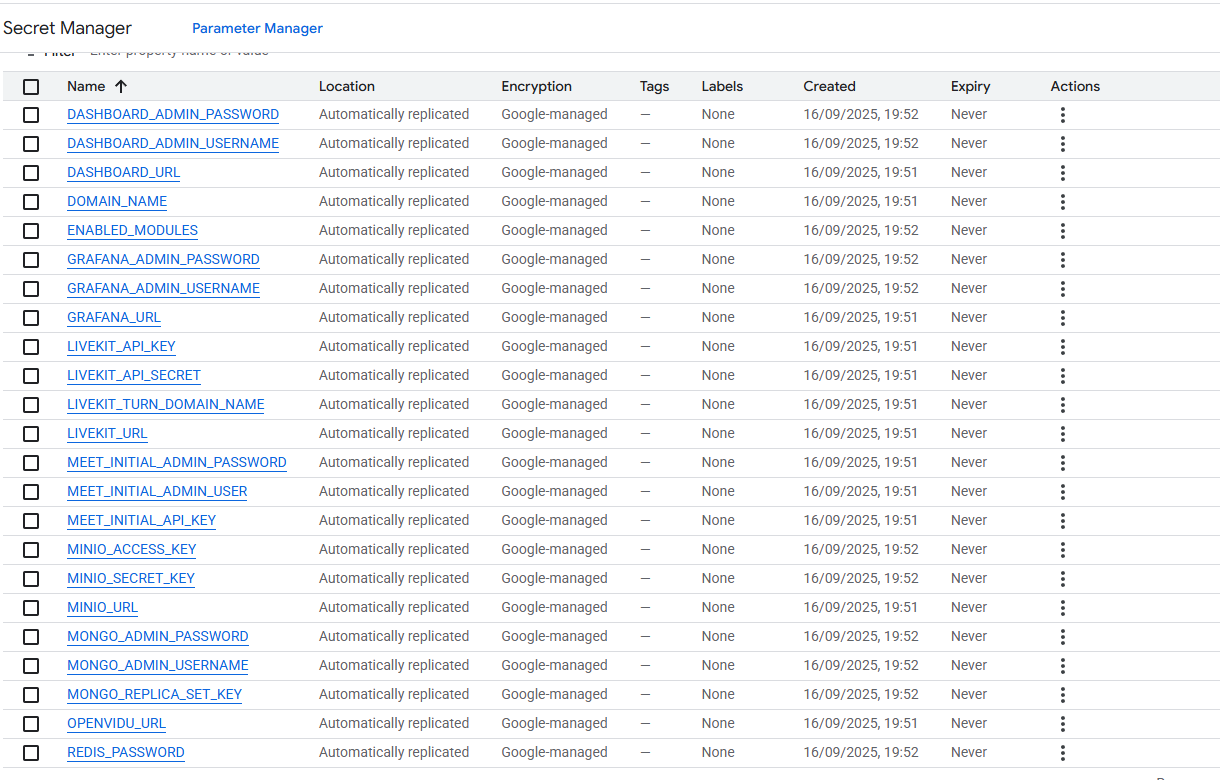
Once you are in the Secret Manager you will see all the secrets by their name.
-
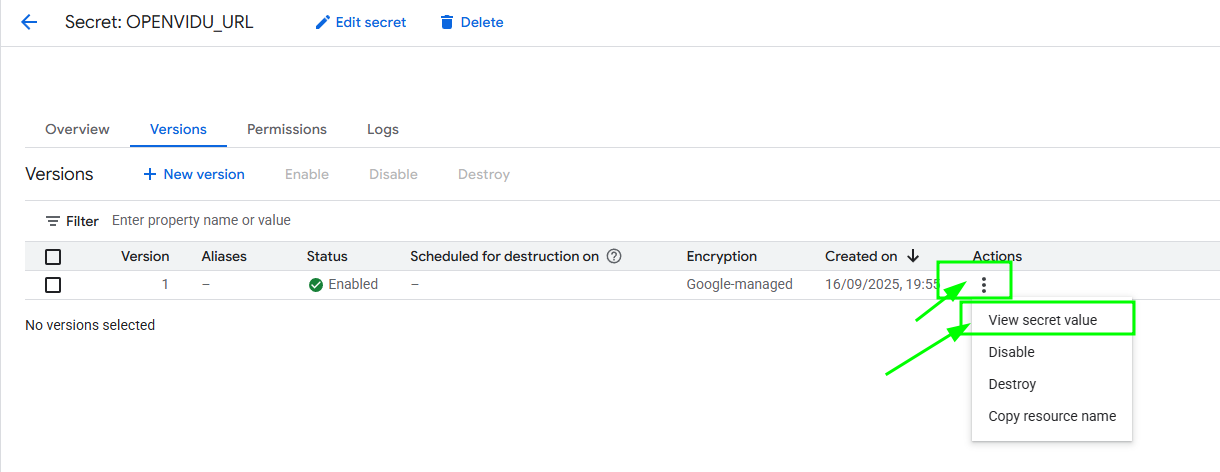
Here click on the secret of your choice, choose the last version and then click on the "3 dots" -> "View secret value" to retrieve that secret.
SSH to any of the Master Nodes by gcloud command generated in the web console and navigate to the config folder /opt/openvidu/config/cluster. Files with the deployment outputs are:
openvidu.envmaster_node/meet.env
To find out the command go to Compute Engine Instances and click on the arrow close to the SSH letters and then "View gcloud command".

To install gcloud in your shell follow the official instructions .
Configure your application to use the deployment#
You need the secret outputs from Google Cloud Platform to configure your OpenVidu application. You can check these secrets in Secret Manager using either of these two methods: (Check deployment outputs in GCP Secret Manager) or (Check deployment outputs in the instance).
Your authentication credentials and the URL to point your applications to are:
OpenVidu Meet:
OPENVIDU_URL: The URL to access OpenVidu Meet, which is alwayshttps://yourdomain.example.io/MEET_INITIAL_ADMIN_USER: User to access OpenVidu Meet Console. It is alwaysadmin.MEET_INITIAL_ADMIN_PASSWORD: Password to access OpenVidu Meet Console.MEET_INITIAL_API_KEY: API key to use OpenVidu Meet Embedded and OpenVidu Meet REST API.
Note
The MEET_INITIAL_ADMIN_USER, MEET_INITIAL_ADMIN_PASSWORD, and MEET_INITIAL_API_KEY values are initial settings that cannot be changed from GCP Secret Manager. They can only be changed from the Meet Console.
OpenVidu Platform:
LIVEKIT_URL: The URL to use LiveKit SDKs, which can bewss://yourdomain.example.io/orhttps://yourdomain.example.io/depending on the client library you are using.LIVEKIT_API_KEY: API Key for LiveKit SDKs.LIVEKIT_API_SECRET: API Secret for LiveKit SDKs.
OpenVidu V2 Compatibility Credentials
This section is only needed if you want to use OpenVidu v2 compatibility.
- URL: The URL to access OpenVidu, which is the value of
OPENVIDU_URL(e.g.,https://yourdomain.example.io/) - Username: Basic auth user for OpenVidu v2 compatibility. It is always
OPENVIDUAPP. - Password: Basic auth password for OpenVidu v2 compatibility is the same as
LIVEKIT_API_SECRET.
Troubleshooting initial Google Cloud Platform deployment creation#
If something goes wrong during the initial GCP deployment creation, your stack may reach some failed status for multiple reasons. It could be due to a misconfiguration in the parameters, a lack of permissions, or a problem with GCP services. When this happens, the following steps can help you troubleshoot the issue and identify what went wrong:
- Check if the instance or instances are running. If they are not, check the GCP cloud build logs for any error messages.
-
If the instance or instances are running, SSH into the instance and check the logs by running this command:
journalctl -u google-startup-scripts | cat
These logs will give you more information about the GCP deployment creation process.
-
If everything seems fine, check the status and the logs of the installed OpenVidu services.
Configuration and administration#
When your Google Cloud Platform deployment reaches the Active state, it means that all resources have been created. You will need to wait about 7 to 12 minutes for the instances to install OpenVidu, as mentioned before. After this time, try connecting to the deployment URL. If it doesn't work, we recommend checking the previous section. Once everything is ready, you can check the Administration section to learn how to manage your deployment.